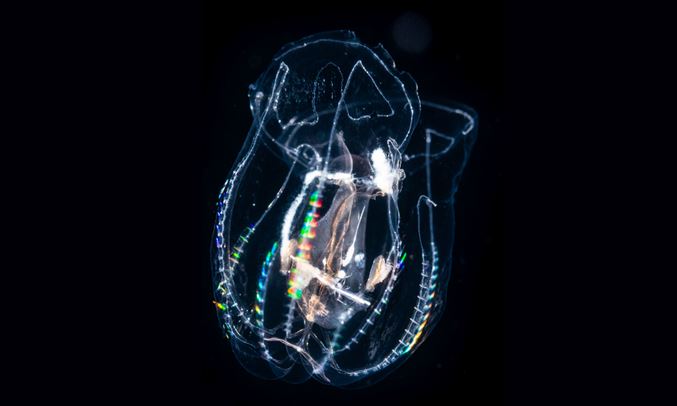
The organism in question has a translucent, pear-shaped body that is slightly flattened in the plane of its tentacles. Notably, the apical organ is not positioned at the aboral (upper) extremity but rather resides in a pit or groove. The species possesses a long, deeply compressed pharynx that tapers towards the aboral end, located near the apical organ. It only has vestigial axial tentacles, confined to the tentacular sheath, and lacks any warts on its body surface.The rows of ctene (comb-like structures used for locomotion) beneath the tentacles, known as subtentacular ctene rows, extend for about half the length of the rows of ctene under the mouth, termed substomodeal ctene rows. Auricles emerge between the oral extremity of the subtentacular comb rows and the end of the oral groove, without extending orally beyond the level of the mouth. The lobes are approximately half the length of the distance between the mouth and the aboral extremity. No gonads were observed in this specimen.